PUC RJ 2019 – EN
PUC – RJ – 2019

The Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro ( PUC-Rio ) is a non-profit, philanthropic, community-based higher education institution of the Secretariat for Regulation and Supervision of Higher Education. Headquartered in Gávea , Rio de Janeiro , Brazil . In current times, it is recognized as one of the best and most prestigious universities in Latin America .
PUC-Rio has two forms of admission for undergraduate courses: the Enem and its own entrance exam. These exams are used to distribute academic scholarships to students.
PUC-Rio was one of the pioneering universities in teaching entrepreneurship in undergraduate courses in Brazil.

01-(PUC – RIO – 019)

From the ground, a ball is thrown vertically upwards and reaches a height of 3.2 meters. How long, in seconds, does the ball take to rise and return to ground level?
Neglect air resistance. Given: g = 10 m/s 2 .
A) 0.32 B) 0.64 C) 0.80 D) 1.6 E) 3.2
02-(PUC – RIO – 019)

A potential difference V is applied to a resistor of resistance R. The power dissipated in this resistor is P.
By doubling the resistance and tripling the potential difference, the new power dissipated will be:
A) 6P B) 3P C) P D) 2P E) 9P/2
03-(PUC – RIO – 019)

Inside a perfect calorimeter, with capacity C = 40 cal/ g o C and initial temperature 0 o C, 100 g of a material with specific heat of 0.50 cal/g o C at a temperature of 90 o C , and a mass of 10 g of ice at 0 o C are placed.
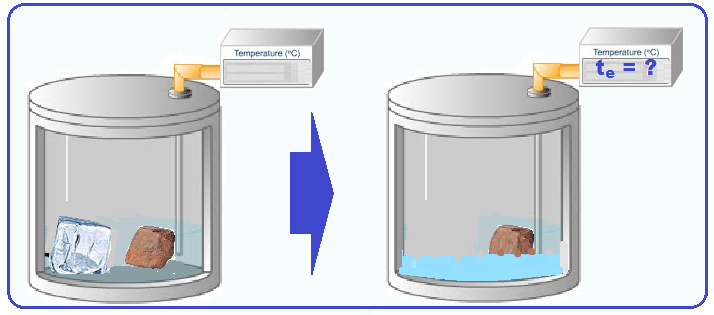
Calculate, in o C, the value of the final equilibrium temperature of the system.
Data: C WATER = 1.0 cal/g C L ICE MELTING = 80 cal/g
A) 40 B) 39 C) 38 D) 37 E) 36
04-(PUC – RIO – 019)

On vacation, a couple takes a car trip, leaving Rio de Janeiro towards Tiradentes .
The first section, on BR-101 to Barbacena , is done at an average speed of 70 km/h.
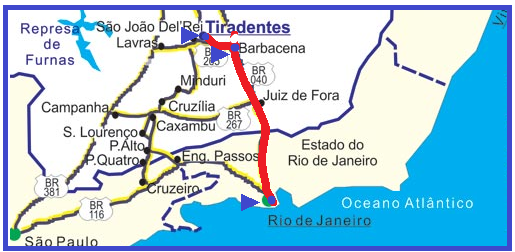
The couple stops for a snack for half an hour and continues their journey taking the BR-265 to Tiradentes , a 60 km stretch that they cover in 60 minutes . The total travel time is 5h30min. Calculate, in km/h, the average speed of the car on the entire Rio-Tiradentes route.
A) 60 B) 62 C) 65 D) 68 E) 70
05-(PUC – RIO – 019)

A 20 kg box is placed on the edge of a truck bed, 1.0 m above the floor. A man places a 2.0 m long wooden board from the edge of the bed to the floor. He gives the box a slight push and it slides down the board at a constant speed until it reaches the floor.
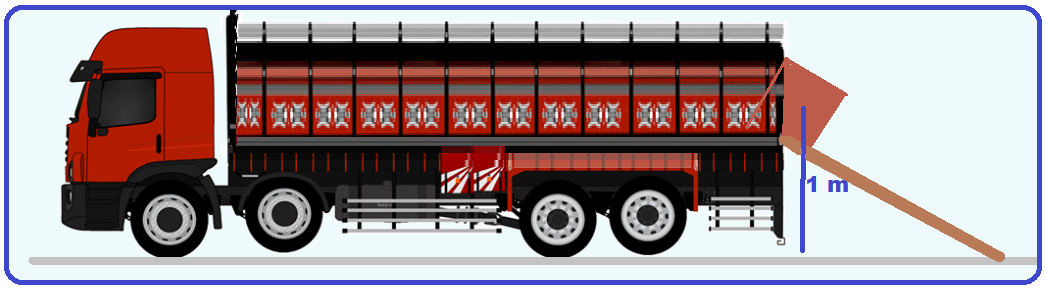
Calculate, in J, the magnitude of the work done by the friction force exerted by the board on the box during its descent .
A) 20 B) 40 C) 100 D) 200 E) 400
06-(PUC – RIO – 019)

Three bodies, 1, 2 and 3, with masses m 1 = 10 kg, m 2 = 15 kg and m 3 = 25 kg, move horizontally on a track on the infinite x axis, without any resistance or friction, with initial velocities v 1 = 4.0 m/s, v 2 = -2.0 m/s and v 3 = 0.0 m/s, respectively.
The initial distance between blocks 1 and 2 is 1.0 m and between blocks 2 and 3 is 2.0 m, as shown in the figure.
Bodies 1 and 2 undergo a completely inelastic collision, that is, they stick to each other after colliding. This set then collides elastically with body 3.

Calculate the speed of body 3, in m/s, after 153 s from the initial instant.
A) 4.00 B) 2.00 C) 0.40 D) 0.20 E) 0.00
07-(PUC – RIO – 019)

A battery supplies a voltage V B and has an internal resistance r. Placing the battery in contact with a voltmeter, the measurement is 12 V. Then placing an ammeter in series with the battery and with a resistor R = 1.0 kΩ, the measurement is 8 mA.
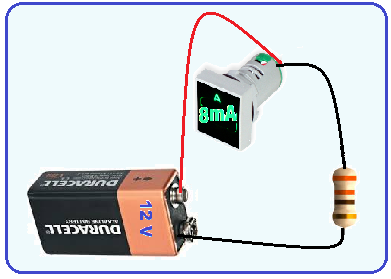
From these measurements, the values of the voltage V B and the internal resistance r, in V and kΩ, are respectively:
A) 12 and 0.50
B) 24 and 1.0
C) 12 and 1.0
D) 24 and 0.50
E) 12 and 2.0
08-(PUC – RIO – 019)

Let the following statements be true:
I. The higher the frequency of a light wave in a vacuum, the higher the speed of propagation of that wave.
II. In a string with both ends fixed, standing waves can only be produced if the length of the string is a multiple of the wavelength.
III. Sound waves need a material medium to propagate and are longitudinal in the air. Select the correct option:
A) Only statement I is true.
B) Only statement II is true.
C) Only statement III is true.
D) Only statements I and II are true.
E) Only statements I and III are true.
Commented resolution of Physics questions from PUC – RIO – 2019
01-
Vertical upward launch
Consider a body thrown vertically upwards , from a point A (origin), with initial scalar velocity Vo . 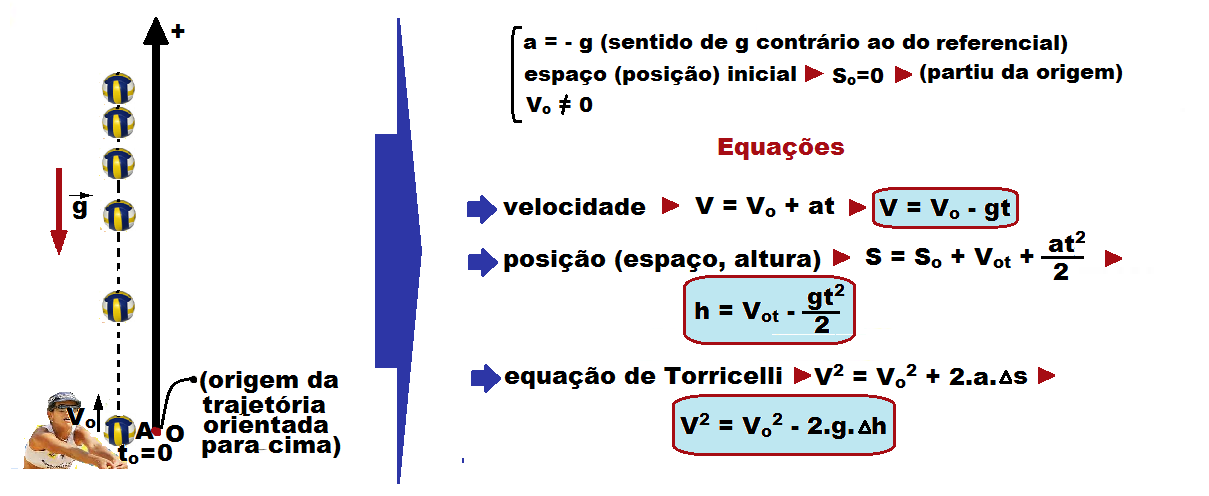

![]() The ascent time is equal to the descent time.
The ascent time is equal to the descent time.
![]() The launch speed (Vo) at the origin is equal to the same speed at the arrival at the origin , but of opposite sign (-Vo).
The launch speed (Vo) at the origin is equal to the same speed at the arrival at the origin , but of opposite sign (-Vo).
![]() At any point on the trajectory, the body has two velocities of the same magnitude, a positive one when going up and a negative one when going down.
At any point on the trajectory, the body has two velocities of the same magnitude, a positive one when going up and a negative one when going down.
![]() If a mobile A leaves a time x before a mobile B, we have: tA – tB = x
If a mobile A leaves a time x before a mobile B, we have: tA – tB = x ![]() tA = tB + x, which must be substituted into the time functions of space or speed to continue solving the exercise.
tA = tB + x, which must be substituted into the time functions of space or speed to continue solving the exercise.
In the case of the exercise, h = 3.2 m and g = 10 m/s 2 at maximum height V = 0 calculation of the launch speed by Torricelli V 2 = V o 2 – 2.gh 0 2 = V o 2 – 2.10.3.2 V o 2 = 64 V o = 8 m/s. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Time it takes to reach maximum height ![]() V = V o – at
V = V o – at ![]() 0 = 8 – 10t
0 = 8 – 10t ![]() t = 8/10
t = 8/10 ![]() t = 0.8 s.
t = 0.8 s.
Since friction is neglected, the ascent time is equal to the descent time ![]() t total = 0.8 + 0.8
t total = 0.8 + 0.8
T total = 1.6 s.
R-D
02-
If you haven’t mastered the theory, here it is:

If you double the resistance value the power will be 2 times lower and if you triple the ddp the power will be 3 2 = 9 times higher ![]() P’ = 9P/2.
P’ = 9P/2.
R- And
03-
Container passing from t o = 0 o C to t e Q 1 = C.(t e – t o ) = 40.(t e – 0) Q 1 = 40t e ![]()
![]()
Material passing from to = 90 o C to t e Q 2 mc .(t e – t o ) = 100.0.5.(t e – 90) Q 2 = 50t e – 4500 ![]()
![]()
Ice at 0 ° C melting (going from ice at 0 ° C to water at 0 ° C) ![]() Q 3 = mL = 10.80
Q 3 = mL = 10.80 ![]() Q 3 = 800 cal
Q 3 = 800 cal
Water passing from t o = 0 o C to t e Q 4 = mc(t e – t o ) = 10.1.(t e – 0) Q 4 = 10t e . ![]()
![]()
As the calorimeter is perfect, there is no heat exchange with the external environment and the sum of the amounts of heat exchanged between them must be zero ![]() 40t e + 50t e – 4500 + 800 + 10t e = 0 100t e = 3700
40t e + 50t e – 4500 + 800 + 10t e = 0 100t e = 3700 ![]()
![]()
t e = 3700/100 ![]() t e = 37 o C.
t e = 37 o C.
R-D
04-
The second section from Barbacena to Tiradentes has a distance of d 2 = 60 km and is covered in t 2 = 60 min = 1 h.
Since he stopped for 0.5 h at the restaurant, and the total travel time was 5h30min = 5.5 h , the first leg of the journey was completed in t 1 = 5.5 h (total time) – (1 h “first leg” + 0.5 h “restaurant”) = 5.5 – 1.5 ![]() t 1 = 4 h (time to travel the first leg).
t 1 = 4 h (time to travel the first leg).
First section ![]() V 1 = d 1 /t 1 70 = d 1 /4 d 1 = 280 km.
V 1 = d 1 /t 1 70 = d 1 /4 d 1 = 280 km. ![]()
![]()

Total average speed = total distance/total time (including stopping ) ![]() V mt = (280 + 60)/5.5 = 340/5.5
V mt = (280 + 60)/5.5 = 340/5.5 ![]() V mt = 61.8 km/h.
V mt = 61.8 km/h.
R-B
05-
As the box descends at a constant speed, the kinetic energy (E c = mV 2 /2) is the same throughout the entire path and the work done by the friction force corresponds to the variation in gravitational potential energy , since the normal force does not do any work (W N = Fdcos90 o = Fd0 = 0).
![]()
R-D
06-
First, inelastic collision between 1 and 2 moving together with common velocity V after the collision:
Since friction is neglected, they move at constant speeds.
Using the principle of conservation of momentum:

Momentum of movement of the system before the collision ![]() Q sa = m 1 V 1 + m 2 V 2 = 10.4 + 15.(-2)
Q sa = m 1 V 1 + m 2 V 2 = 10.4 + 15.(-2) ![]()
Q sa = 10 kg.m/s.
Amount of movement of the system after the collision when they move together with a common velocity V ![]() Q sd = m 1 V + m 2 V = 10.V + 15.(V)
Q sd = m 1 V + m 2 V = 10.V + 15.(V) ![]() Q sd = 25V.
Q sd = 25V.
Q sa = Q sd 10 = 25V V = 10/25 V = 0.4 m/s (common speed of blocks 1 and 2 after the collision). ![]()
![]()
![]()
Second collision between blocks 1 and 2, considered as a single block with mass m 12 = (10 + 15) = 25 kg and block 3 with mass m 3 = 25 kg.
Since the collision is elastic (coefficient of restitution is 1) and they have the same mass ,
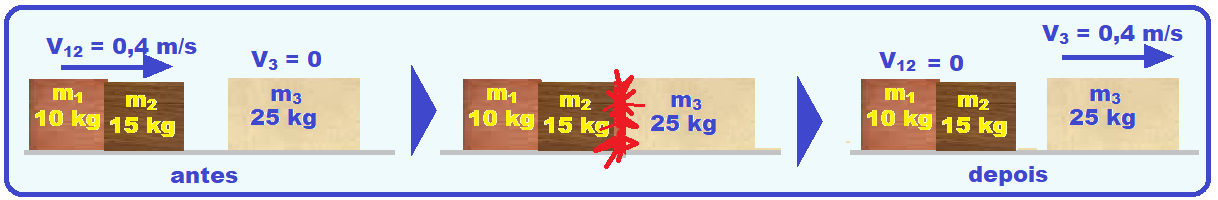
exchange their speeds after the collision and, thus, the block with mass m 12 remains stationary (V = 0) and block 3 moves at a constant speed of V 3 = 0.4 m/s.
If friction is ignored, after any instant (including 153 s) this speed will be the same.
R-C
07-
When the voltmeter is placed in contact with the battery poles and indicates 12 V, it will be providing the value of the electromotive force E of the battery ![]() E = 12 V.
E = 12 V.
The ddp, voltage or voltage U at the terminals of the resistor of R = 1 kΩ = 1.10 3 Ω, traversed by i = 8 mA = 8.10 -3 A (ammeter indication ) will be ![]() R = U/i
R = U/i ![]() 10 3 = U/8.10 -3 U = 8 V.
10 3 = U/8.10 -3 U = 8 V. ![]()
Generator equation U = E – ri ![]() 8 = 12 – r.8.10 -3 r = 4/8.10 -3 r = 0.5 .10 3 = 0.5 kΩ.
8 = 12 – r.8.10 -3 r = 4/8.10 -3 r = 0.5 .10 3 = 0.5 kΩ. ![]()
![]()
A- A
08-
I. False ![]() the speed of light (and any other electromagnetic wave) in a vacuum is constant and is V = c = 3.10 8 m/s, regardless of frequency.
the speed of light (and any other electromagnetic wave) in a vacuum is constant and is V = c = 3.10 8 m/s, regardless of frequency.
II. False![]()

They must have the same wavelength.
III. True

R-C
