CONCEPTS ABOUT NEWTON’S LAWS
Commented Resolution
Concepts about Newton’s Laws
01- The ship is in space (vacuum) free from gravitational forces — initially, when the ship moves from X to Y at constant speed (MRU), the resultant of all the forces acting on it is zero (consequence of the principle of inertia) — when the lateral engine is activated, a lateral force appears on the ship pulling it to the south but, at the same time, by inertia it continues to move to the east, making a movement in the southeast direction — when it reaches position Z (moving in the southeast direction) the engine is turned off and the resultant of the forces acting on the ship becomes zero and, by inertia, it moves in MRU in the southeast direction —
A- A
02- Inertia in liquids — the liquid in the container on the left in the figure below is in equilibrium (horizontal level). If a resulting force to the right appears on it, accelerating it, due to inertia, the liquid level will acquire the shape shown in the figure on the right.
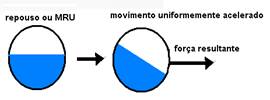
– On the other hand, if the container + liquid are moving at a constant speed to the right and a resulting force appears on it to the left, braking it, the liquid, by inertia, will acquire the shape of the figure on the right.
– The system of communicating vessels in the figure on the left below is in equilibrium (liquid at the horizontal level).
If the system is accelerated to the right by a resulting force, by inertia, the liquid will acquire the shape of the figure on the right (observe it carefully) — R- B
03- Every body that has mass has inertia defined as “Any body that is at rest or in rectilinear and uniform motion (moving in a straight path with constant vector velocity), tends to continue in these states if the resulting force acting on it is zero” — R- B
04- You wear a seat belt in a car because if it stops quickly, for example, in a crash, you, for example,
inertia, tends to maintain the same speed that the car had at the moment of the collision and would be thrown forward, which does not happen, as the belt applies the external force to it — R- B
05- Statement III is wrong, because in all circular motion the vector velocity is variable —
even if the intensity is constant, the direction and sense of the velocity vector vary, as it is always tangent to the trajectory at each point — R- B
06- An ideal dynamometer inserted into an ideal rope (inextensible and of negligible mass), indicates the intensity of the tensile force at each of its ends (figure below).
If we have two or more dynamometers connected as shown in the figure below and at the free end of the dynamometer on the right we apply a force, for example 20N, each dynamometer will indicate 20N.
R-D
07- Observe in the figure below, that = + and that, = + .
Since the resultant force is the vector sum of all the forces you have
08- Calculation of the acceleration of the cube of side L — ΔS=V o t + at 2 /2 — 80=0 + a. 10 2 /2 — a=1.6m/s 2 — as the new cube is identical to the previous one, they have the same density — d=m/v — d=m/(L/2)3 — note in the previous expression that, if the volume becomes 8 times smaller, the mass will also become 8 times smaller, since the density is constant — F=ma — since the force F is the same, if the mass becomes 8 times smaller, the acceleration must become 8 times greater — new acceleration — a=8×1.6 — a=12.8m/s 2 — ΔS’=V o t + at 2 /2 = 0 + 12.8 . 10 2 /2 — ΔS’=640m — R- C
09- If the plane accelerates forward, by inertia, the body hanging from the wire tends to remain still in relation to the runway and, therefore, goes backwards in relation to the plane — the wire tilts to the left — the acceleration of the plane will be given by — a = g.tan 25 o = 10.0.47 — a = 4.7 m/s² — R- A
10- Statement I corresponds to the principle of action and reaction involving field forces (where there is no contact) and IV also refers to the principle of action and reaction involving contact forces — R- D
11- a) False — the trajectory of the center of mass is close to a parabola and does not cross at any point.
b) False — the opposite, the ball will travel a shorter distance, due to the rotation movement it will tend to go lower — topspin corresponds to the feat achieved by hitting the ball from bottom to top, which causes it, after bouncing on the ground, to gain acceleration towards the back of the court. Often used by players who prefer to play on the baseline.
c) Correct – Newton’s Law of Action and Reaction.
d) Incorrect – Kinetic energy is acquired in the downward movement and potential energy in the upward movement.
e) Incorrect – Torques provide rotational movements.
R-C
12- As the sets are in balance, the resulting forces on the athlete, in any case, are zero — note that in the last situation the tensions cancel each other out, but their intensities are greater than in the first and second situations — R- D
13- When the bus moves in one direction, by inertia, the passenger is thrown in the opposite direction — P – left, Q – right, R – right and S – left.
R-B
14- The forces that constitute the action and reaction pair exchanged between two bodies always have the same intensity , same direction and opposite senses, regardless of their masses — R- C
15- The forces of interaction between the star and the planet constitute a pair of action and reaction whose action occurs at considerable distances (field forces) — R- B
16- If the fly moves vertically, its wings will apply vertical forces to the air inside the balloon, unbalancing the system — A- A
17- Note that the fan and the sail are fixed to the same boat (same body) and the principle of action and reaction is only valid when forces are exchanged between different bodies — R- D