Potência elétrica – Energia elétrica EN
ELECTRICAL POWER – ELECTRICAL ENERGY
Electrical power – Electrical energy
Energy
![]() Typically, the concept and use of the word energy refers to the ability to perform work or perform an action. It can take several forms: potential, mechanical, chemical, electromagnetic, electrical, thermal, etc.
Typically, the concept and use of the word energy refers to the ability to perform work or perform an action. It can take several forms: potential, mechanical, chemical, electromagnetic, electrical, thermal, etc.
The term energy can also designate reactions due to a certain form of work , for example, heat, mechanical work (movement) or light .
These can be carried out by an inanimate source (e.g. engine, boiler, refrigerator, speaker, lamp, shower, fan) or by a living organism such as muscles, biological energy, etc.
Electric energy
 Electrical energy or electricity is the name given to phenomena involving electrical charges.
Electrical energy or electricity is the name given to phenomena involving electrical charges. ![]()
All electrical appliances require electrical energy to operate.
When they receive this energy , they transform it into another form of energy. Thus, a fan transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy and thermal energy ; a filament bulb

transforms electrical energy into light and thermal energy ; an electric shower transforms electrical energy into thermal energy, etc.
Electrical power
 The greater the amount of energy transformed in a given unit of time, the greater the power of the device. Therefore, electrical power is a quantity that measures the speed at which electrical energy is transformed into another (or other) form of energy , in a given unit of time.
The greater the amount of energy transformed in a given unit of time, the greater the power of the device. Therefore, electrical power is a quantity that measures the speed at which electrical energy is transformed into another (or other) form of energy , in a given unit of time.
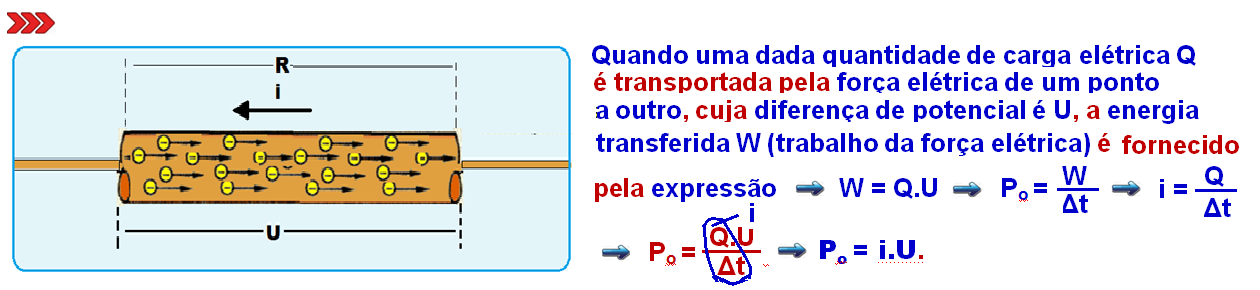
Electrical power ( Po ) is defined as the ratio between the electrical energy transformed or transferred (W) and the time interval (Δt) of this transformation.

Note in the expression above that the greater the power of a device, the greater the amount of energy dissipated by it.
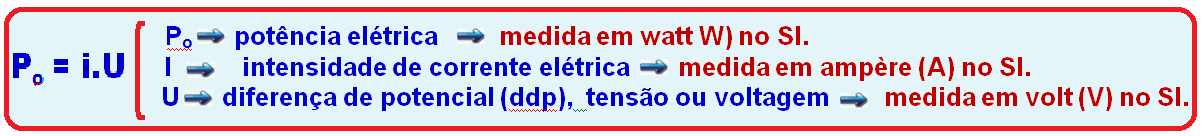
Relationship between electrical power (P o ), electrical current (i) and potential difference, voltage or strain U

Electricity consumption (W)
The joule (J) is a very small unit of electrical energy , used to measure the electrical energy consumption of homes, buildings, factories, etc.
Since this measurement, in joules (J) is expressed by a very large number , in practice the kilowatt-hour (kWh) is used , whose relationship with the joule is as follows W = P o .Δt 1kWh = ![]()
![]()
1000W.1h = 1,000W.3,600s ![]() 1kWh = 3.6.106 J 1 kW.h is the amount of energy dissipated by an electrical appliance with a nominal power of 1,000 Watts, operating for one hour .
1kWh = 3.6.106 J 1 kW.h is the amount of energy dissipated by an electrical appliance with a nominal power of 1,000 Watts, operating for one hour . ![]()
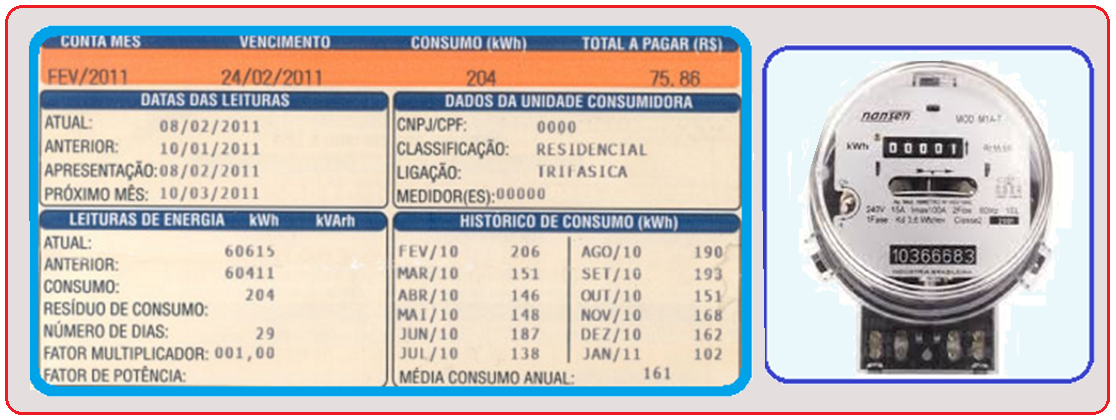
Electricity meters and their respective consumption are expressed in kWh.
What you should know, information and tips
![]()



 1kWh = 3.6.106 J 1 kW.h is the amount of energy dissipated by an electrical appliance with a nominal power of 1,000 Watts, operating for one hour (3,600s).
1kWh = 3.6.106 J 1 kW.h is the amount of energy dissipated by an electrical appliance with a nominal power of 1,000 Watts, operating for one hour (3,600s). ![]()
 An incandescent lamp with P o = 100 W and U = 127 V has the same brightness as a fluorescent lamp with P o = 25 W and U = 127 V, but the P o = 25 W lamp dissipates less power and consequently consumes less electrical energy.
An incandescent lamp with P o = 100 W and U = 127 V has the same brightness as a fluorescent lamp with P o = 25 W and U = 127 V, but the P o = 25 W lamp dissipates less power and consequently consumes less electrical energy.

All packaging must include: Manufacturer’s brand, power (W), voltage (V), efficiency (in
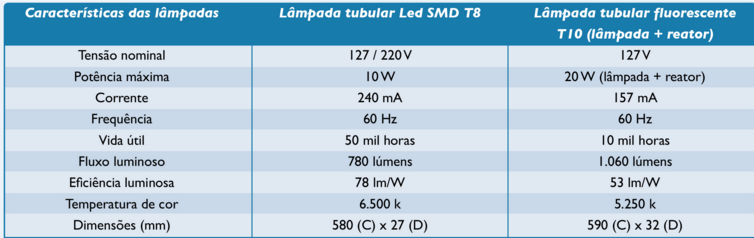
lumens per Watts (lm/W) and effective current (A).
